Network Traffic in Elastic Beanstalk visualised
In Beanstalk there are 2 primary ways of configuring HTTPs, we will visualise both and demistify different ports used by default when combining Nginx and Docker.
Both approaches to configuring HTTPs have their own advantages, the most common way is to terminate HTTPs Traffic at ALB as it’s easier to setup while maintaining scalablility
Traffic via ALB
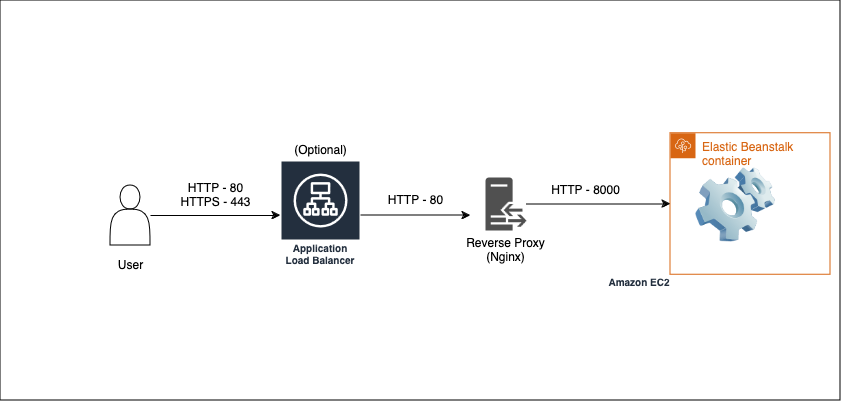
When a user tries connecting to the Elastic Beanstalk their first stop will be ALB to which traffic will be encrypted next ALB will need to forward traffic directly to the instance in a non encrypted form which will be recieved by the Reverse Proxy. On Elastic Beanstalk the default proxy is Nginx however you can configure Elastic Beanstalk to use Apache instead.
Advantages:
- There is no need to manage HTTPs certificate as it can be auto-renewed (provided that your domain is within AWS Route 53)
- (optional) You can add AWS WAF on top of the Load Balancer
- Allows for distributing the traffic more equally between the instances
- Less computing power needed as instance does not need to decrypt incoming HTTPs traffic
You can find the ports for the Nginx which were visualised in the graph above via the 2 commands listed below
The port on which Nginx itself is listening:
$ cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf | grep "listen 80" -A 20 -B 1
server {
listen 80 default_server; #<--- HERE
gzip on;
gzip_comp_level 4;
gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/x-javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
location / {
proxy_pass http://docker;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
# Include the Elastic Beanstalk generated locations
include conf.d/elasticbeanstalk/*.conf;
}
The port on which Docker Application itself should be running:
$ cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/elasticbeanstalk-nginx-docker-upstream.conf
upstream docker {
server 172.17.0.2:8000; #<--- HERE
keepalive 256;
}
Direct to instance
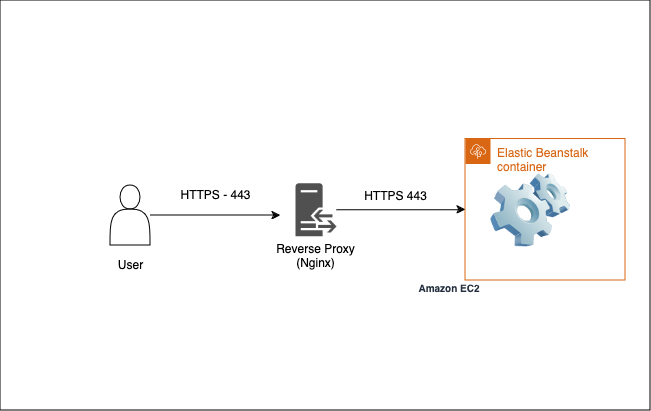
You can configure the terminate at instance HTTPS in Docker via following link or for other Platform types use this link instead
Advantages:
- Higher level of security, as we prevent any middleman attacks from inside of the VPC
- Cheaper as we do not require ALB to be present to serve our traffic